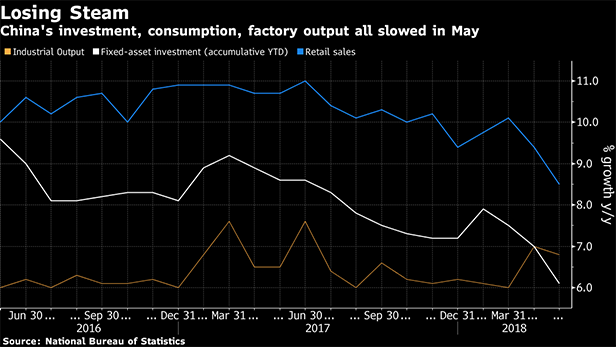
Trade tensions between the world's two biggest economies intensified, with China vowing to retaliate “forcefully” against President Donald Trump's threatened tariffs on another $200 billion in Chinese imports.“If the U.S. loses its senses and publishes such a list, China will have to take comprehensive quantitative and qualitative measures,” according to a statement from the Ministry of Commerce. It labeled the move “extreme pressure and blackmail,” and said it would retaliate with counter measures.Trump ordered up identification of $200 billion in Chinese imports for additional tariffs of 10 percent—with another $200 billion after that if Beijing retaliates. While the $50 billion in tariffs already announced on Friday were mainly on industrial goods, the broader move would push up prices for toys, tools, t-shirts, and a lot more for U.S. shoppers.Equities fell around the world as economists warned of damaged business confidence, a blow to China's growth prospects, and ripple effects through its supply chains. The S&P 500 Index slipped 0.9 percent at 9:58 a.m. in New York. The benchmark index of Chinese stocks fell almost 4 percent, other Asian share markets declined. Safe havens including the yen, gold, and Treasuries climbed.“Its psychological effects, its effects in increasing uncertainty, could be very serious and we're certainly getting later in a cycle of escalation,” former U.S. Treasury Secretary Lawrence Summers said in an interview on Bloomberg Television.By targeting goods that are finished in China but whose components are often sourced from neighboring South Korea, Japan, Taiwan, and more, the U.S. strategy could hurt the economies of America's allies too."The collateral damage from an escalating U.S.-China trade war will be widespread, hitting many Asian countries that are part of China's manufacturing supply chain in sectors such as electrical and electronic products," said Rajiv Biswas, Asia-Pacific chief economist at IHS Markit in Singapore.There are dangers for the U.S. economy too. If implemented, the tariffs would mean a sizable amount of imported Chinese goods would be exposed to new tariffs. Higher prices on imported goods could dampen consumer sentiment and pressure inflation.“In a global trade war, no matter how you spin tariffs, retailers and the American families that we serve are the losers,” said Hun Quach, vice president, international trade, for the Retail Industry Leaders Association.Tom Orlik, chief economist at Bloomberg Economics, said that in the event that China's exports to the U.S. weaken in the face of tariffs, the government would likely seek to offset the growth impact with a combination of subsidies to support domestic demand and higher infrastructure investment.The People's Bank of China is using both money and words to try to ease market concerns about escalating trade tensions and the weakening economy. It injected another 200 billion yuan ($31 billion) into the economy via its medium-term lending facility on Tuesday, pushing its net injections so far in June to the most in any month since December 2016.The escalation in trade tensions comes at an inopportune time for China's policymakers, with indicators for May suggesting growth is already dialing back a notch.
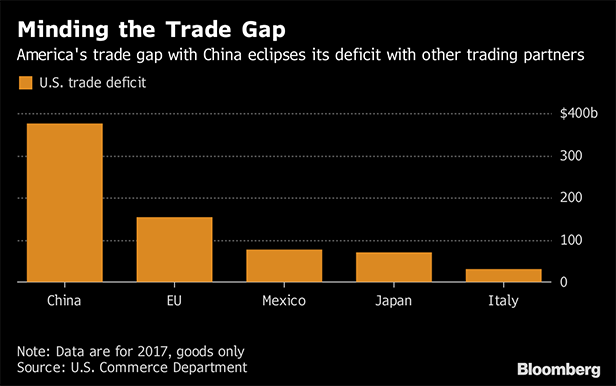
The U.S. president last week threatened 25 percent tariffs on $50 billion in Chinese products and said at the time he would impose even more duties if China retaliated. A counter punch was swift in coming, with a statement from Beijing on Friday night that it would "strike back forcefully."China's threat “clearly indicates its determination to keep the United States at a permanent and unfair disadvantage,” Trump said Monday. “This is unacceptable. Further action must be taken to encourage China to change its unfair practices, open its market to United States goods, and accept a more balanced trade relationship.”The latest salvo came as Trump seeks to convince U.S. lawmakers to let Chinese telecom company ZTE Corp. remain in business after it became a bargaining chip in the trade row. Earlier this month, the Trump administration gave ZTE a reprieve for breaking a sanctions settlement after the company agreed to pay fines, change management, and agree to American oversight. ZTE's survival has been a key goal of Chinese President Xi Jinping.Shares in ZTE declined after the Senate passed legislation on Monday evening that would restore penalties.The U.S. imported $505 billion of goods from China last year and exported about $130 billion, leaving a 2017 trade deficit of $376 billion, according to U.S. government figures. The fact that America imports more from China will make it harder for Beijing to match Trump's attacks, according to Derek Scissors, a resident scholar at the conservative American Enterprise Institute in Washington who focuses on China.
“All they can do is impose higher tariffs on a smaller subset of products,” he said. That being said, “China is going to retaliate,” he added.
Copyright 2018 Bloomberg. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed.
 The U.S. president last week threatened 25 percent tariffs on $50 billion in Chinese products and said at the time he would impose even more duties if China retaliated. A counter punch was swift in coming, with a statement from Beijing on Friday night that it would "strike back forcefully."China's threat “clearly indicates its determination to keep the United States at a permanent and unfair disadvantage,” Trump said Monday. “This is unacceptable. Further action must be taken to encourage China to change its unfair practices, open its market to United States goods, and accept a more balanced trade relationship.”The latest salvo came as Trump seeks to convince U.S. lawmakers to let Chinese telecom company ZTE Corp. remain in business after it became a bargaining chip in the trade row. Earlier this month, the Trump administration gave ZTE a reprieve for breaking a sanctions settlement after the company agreed to pay fines, change management, and agree to American oversight. ZTE's survival has been a key goal of Chinese President Xi Jinping.Shares in ZTE declined after the Senate passed legislation on Monday evening that would restore penalties.The U.S. imported $505 billion of goods from China last year and exported about $130 billion, leaving a 2017 trade deficit of $376 billion, according to U.S. government figures. The fact that America imports more from China will make it harder for Beijing to match Trump's attacks, according to Derek Scissors, a resident scholar at the conservative American Enterprise Institute in Washington who focuses on China.
The U.S. president last week threatened 25 percent tariffs on $50 billion in Chinese products and said at the time he would impose even more duties if China retaliated. A counter punch was swift in coming, with a statement from Beijing on Friday night that it would "strike back forcefully."China's threat “clearly indicates its determination to keep the United States at a permanent and unfair disadvantage,” Trump said Monday. “This is unacceptable. Further action must be taken to encourage China to change its unfair practices, open its market to United States goods, and accept a more balanced trade relationship.”The latest salvo came as Trump seeks to convince U.S. lawmakers to let Chinese telecom company ZTE Corp. remain in business after it became a bargaining chip in the trade row. Earlier this month, the Trump administration gave ZTE a reprieve for breaking a sanctions settlement after the company agreed to pay fines, change management, and agree to American oversight. ZTE's survival has been a key goal of Chinese President Xi Jinping.Shares in ZTE declined after the Senate passed legislation on Monday evening that would restore penalties.The U.S. imported $505 billion of goods from China last year and exported about $130 billion, leaving a 2017 trade deficit of $376 billion, according to U.S. government figures. The fact that America imports more from China will make it harder for Beijing to match Trump's attacks, according to Derek Scissors, a resident scholar at the conservative American Enterprise Institute in Washington who focuses on China. “All they can do is impose higher tariffs on a smaller subset of products,” he said. That being said, “China is going to retaliate,” he added.
“All they can do is impose higher tariffs on a smaller subset of products,” he said. That being said, “China is going to retaliate,” he added.



