The ties that bind the global economy together—and deliver goods in abundance around the world—are unraveling at a frightening pace.
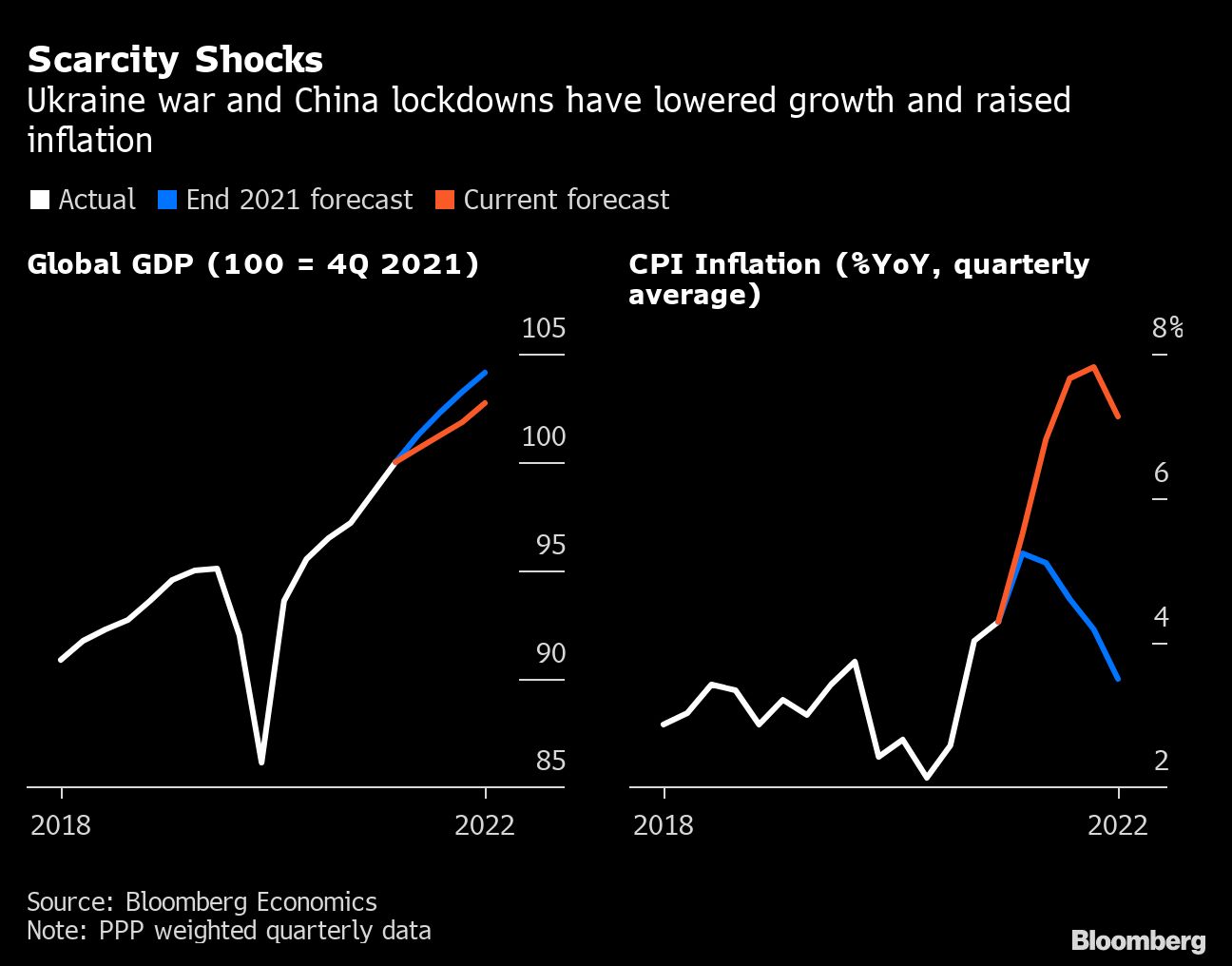
Russia's invasion of Ukraine and China's Covid Zero lockdowns are disrupting supply chains, hammering growth, and pushing inflation to 40-year highs. They're the chief reasons why Bloomberg Economics has lopped $1.6 trillion off its forecast for global gross domestic product (GDP) in 2022.
Recommended For You
But what if that's just an initial hit? War and plague won't last forever. But the underlying problem—a world increasingly divided along geopolitical fault lines—only looks set to get worse.
Bloomberg Economics has run a simulation of what an accelerated reversal of globalization might look like in the longer term. It points to a significantly poorer and less productive planet, with trade back at the same levels as before China joined the World Trade Organization (WTO). An additional blow: Inflation would likely be higher and more volatile.
Supply-Chain Fragmentation Is 'Going to Stay'
For investors, a world of nasty surprises on growth and inflation offers little to cheer equities or bond markets. So far in 2022, commodities—where scarcity drives prices higher—have been among the big winners, along with companies that produce or trade them. Shares in defense firms have outperformed too, as global tensions have soared.
"Fragmentation is going to stay," says Robert Koopman, the WTO's chief economist. He expects a "reorganized globalization" that will come with a cost: "We won't be able to use low-cost, marginal-cost production as extensively as we did."

For three decades, a defining feature of the world economy has been its ability to churn out ever more goods at ever lower prices. The entry of more than a billion workers from China and the former Soviet bloc into the global labor market, coupled with falling trade barriers and hyper-efficient logistics, produced an age of abundance for many.
But the past four years have brought an escalating series of disruptions. Tariffs multiplied during the U.S.–China trade war. The pandemic brought lockdowns. And now, sanctions and export controls are up-ending the supply of commodities and goods.
All of these trends risk leaving advanced economies facing a problem they thought they'd vanquished long ago: scarcity. Emerging nations could see more acute threats to energy and food security, like the ones already causing turmoil in countries from Sri Lanka to Peru. And everyone will have to grapple with higher prices.
A few numbers illustrate the scale of the new barriers:
- Tariffs. The trade war saw U.S. charges on Chinese goods rocket from 3 percent to about 15 percent over the course of Donald Trump's presidency.
- Lockdowns. This year's Covid crackdown in China has put hundreds of billions of dollars in exports at risk, and has disrupted supply chains for companies from Apple Inc. to Tesla Inc.
- Sanctions. In 1983, the flows of trade subject to export or import bans were worth only about 0.3 percent of global GDP. By 2019, that share had risen more than fivefold. Sweeping embargoes triggered by Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and efforts by countries to secure their own supplies by barring sales abroad—like India's recent ban on wheat exports—have pushed the figure higher still.

Viewed from one angle, all of this is part of a global rupture that pits Western democracies and free markets against Chinese and Russian authoritarianism. But it's not necessary to believe in a Manichean struggle between good and evil—or expect the rival camps to separate behind a new Iron Curtain—to see the prospective costs.
About $6 trillion worth of goods—equivalent to 7 percent of global GDP—are currently traded between democratic and autocratic countries. To illustrate the risks of the great unraveling, Bloomberg Economics introduced a 25 percent tariff on all that traffic into a model of the global economy. That's equal to the highest rates that the U.S. and China have leveled against each other, and it can stand in for other kinds of friction too, like sanctions and export bans.

The result: In our model, this tariff leads global trade to plunge by some 20 percent relative to a scenario without the decoupling. Trade as a share of global GDP falls back to its levels at the end of the 1990s, before China joined the WTO. That's a huge and wrenching change.
All countries would have to shift resources toward activities they're less good at. A chunk of the productivity that's associated with trade would be lost. In the long term, a rollback of globalization to late-1990s levels would leave the world 3.5 percent poorer than if trade were to stabilize at its current share of output, and 15 percent poorer relative to a scenario in which global ties continue to strengthen.
Moreover, the model shows that another 7 percent of existing trade relationships would shift between blocs. In concrete terms, that might mean factories making goods for U.S. markets would move from China to, say, India or Mexico.
As this example suggests, there would be winners in our scenario. But the transition would take time and cause severe bottlenecks along the way, ushering in a period of high and volatile inflation. As Kenneth Rogoff, then a top economist at the International Monetary Fund (IMF), warned back in 2003: "The global economy now appears immersed in a long wave of low inflation, but experience suggests that many factors, notably heightened conflict that reverses globalization, can bring it to an end."
Rival Camps
To be sure, the reality of global fracture is unlikely to play out along such clear-cut ideological lines as our scenario modeling. Still, our numbers provide a sense of what's at risk.
Democracies can be forgiven for feeling under threat. In 1983, when Ronald Reagan called the Soviet Union an "evil empire," authoritarian countries accounted for about 20 percent of global GDP. Fast-forward to 2022, and that share has risen to 34 percent. In the years ahead, with China expected to outgrow the U.S. and Europe, it will edge higher still.

The war in Ukraine shows rival political systems lining up on opposite sides. Chinese President Xi Jinping remains supportive of his Russian ally Vladimir Putin, while Europe and the United States are aligned on sanctions for Moscow and military support for Kyiv. It also shows the limits of that framing. India, the world's most populous democracy, continues to buy Russian oil and weapons. Many other democracies—in Asia, Latin America, and elsewhere—show little desire to join the U.S.-led campaign of economic and financial pressure on Russia.
Whether they're defined by an ideological divide, or simply diverging interests in a multipolar world, the deepening fault lines are real. China's latest Covid lockdowns are a good example of some of their harder-to-predict consequences.
In a world of friendlier great-power relations, Chinese leaders likely would have acquired enough of the effective U.S.-made Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines to give their population a measure of omicron immunity, allowing the economy to reopen. In a world where China is determined to demonstrate its self-sufficiency and dodge dependence on foreign innovations, they have not.
As a consequence, China's 1.4 billion population has insufficient protection from the virus. Letting omicron rip could cause 1.6 million deaths, a recent study in the journal Nature Medicine found. So Beijing sees little option but to continue with draconian lockdowns. As a result, China is taking a crushing blow to growth. And the rest of the world faces yet more disruption to supply chains, as Chinese factories stall and cargo ships float idle outside Shanghai's port.
Direct Retaliation from China or Russia?
The threat to U.S. and European economies isn't limited to the repercussions of Chinese lockdowns or blowback from their own measures against Russia. They could also be exposed to direct retaliation.

China's 2010 ban on the sale of rare earths—crucial inputs into everything from smart phones to electric-car batteries—to Japan is one example of how export controls can be used by either side. Russia turning off the gas for Poland and Bulgaria is another. If Putin goes further and cuts shipments to Germany, France, and Italy too, the result would put 40 percent of the European Union's (EU's) supply at risk, tipping the bloc from Covid recovery into painful recession.
Even in the depths of the U.S.–China trade war, the idea of an extreme rupture between rival geopolitical camps seemed far-fetched. The degree of interdependence embodied in the supply chains of companies like Apple appeared too great to disentangle. Some argued that the end of the Trump administration would restore normal relations.
In 2022, with the trade war tariffs still in place, the Covid crisis adding to pressure to localize supply chains, and Russia locked out of U.S. and European markets, it doesn't seem so far-fetched.
The intensity of the current shocks from war and plague will fade. The underlying forces driving deglobalization will not. Brace for a world of lower growth, higher prices, and increased volatility.
Methodology and Sources
To estimate the impact of globalization unraveling on international trade flows, Bloomberg Economics used the quantitative international trade model developed by Antras and Chor (2018) and imposed a 25% tariff on all exports of goods and services between countries in the democratic bloc and countries in the autocratic bloc, as classified using the Freedom House's scores.
The impact of lower trade intensity on global output is derived from estimating the historical relationship between globalization (using the KOF institute's aggregate globalization index) and potential GDP (using Bloomberg Economics' estimates for capital deepening and total factor productivity), in the spirit of Del Negro and Primiceri et al. (2015).
The classification of countries between democracies and autocracies is based on Freedom House's Freedom in the World annual reports. Countries with a Global Freedom Score of 50 or above are classified as democracies.
Trade volumes subject to sanctions are calculated as the total of bilateral trade flows exposed to partial or total import or export bans, based on data from the Global Sanctions Data Base (GSDB), Felbermayr et al. (2020).
—With assistance from Brendan Murray, Alex Tribou and Scott Johnson.
© Touchpoint Markets, All Rights Reserved. Request academic re-use from www.copyright.com. All other uses, submit a request to [email protected]. For more inforrmation visit Asset & Logo Licensing.



